Master the Paper Towel Method for Cannabis Seed Germination
Please note that if you are in a country, state, or area where cannabis cultivation is legal, we recommend using the following cannabis seed germination method. We write this article specifically for those in the ACT or overseas. We do not support or endorse the germination of cannabis seeds and sell seeds strictly as souvenirs or collectable items.
This method is also great for all heirloom herb seeds or blue lotus seeds.
This technique delivers higher germination rates, allows for effortless monitoring, and is space-efficient. Our guide not only walks you through how to implement this method for cannabis seeds but also reveals its benefits for a wider range of seeds, complete with troubleshooting tips.
Key Takeaways
- The paper towel method is a widely used germination technique for cannabis seeds due to its ability to provide consistent moisture and temperature, resulting in higher and faster germination rates.
- This method allows for clear visibility and easy monitoring of germination, helping gardeners pick the healthiest seedlings for soil transfer, and it is highly space-efficient, perfect for areas with limited space.
- Although especially effective for cannabis, the paper towel method can also be applied to a variety of other seeds such as vegetables, herbs, and flowers, making it a versatile choice for different types of gardeners.
Why has the paper towel method become such a go-to for germinating seeds, especially cannabis seeds?
The answer lies in three key advantages: improved germination rates, enhanced visibility and control over the germination process, and the superior space efficiency it offers.
Improved Germination rates and speed
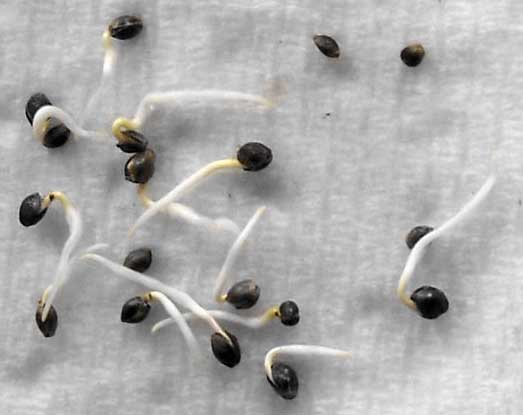
The paper towel method creates an ideal environment for seed germination, fostering successful growth and development. Placing seeds between moist paper towels in a warm location aids in maintaining steady moisture and temperature levels. These conditions are ideal for encouraging seeds to sprout, often leading to higher germination rates compared to planting seeds directly in soil.
Moreover, the regulated heat and moisture conditions inside a plastic baggie can expedite the germination process, often leading to sprouting within a few days. This rapid germination is particularly beneficial for vegetable seeds that traditionally have longer germination times, such as cannabis seeds, asparagus and chili pepper seeds.
Easy Monitoring
The paper towel method offers the following advantages:
- Improved visibility and control over the germination process
- Transparent sandwich bags allow for clear observation of the seeds
- Helps identify and discard any seeds that do not germinate, saving time and resources.
Plus, it also enables gardeners to identify and choose the most vigorous seedlings for transferring to soil using seed starting trays, ensuring they are planted just above the soil line.
Space Efficiency
For gardeners with limited space, the paper towel method is a game-changer. Using paper towels offers the following benefits:
- Takes up very little space compared to traditional seed trays or pots
- Can fit a good 15 or more seeds per bag, maximising usage of available space
- Provides efficiency at its best
Step-by-Step Guide to the Paper Towel Method
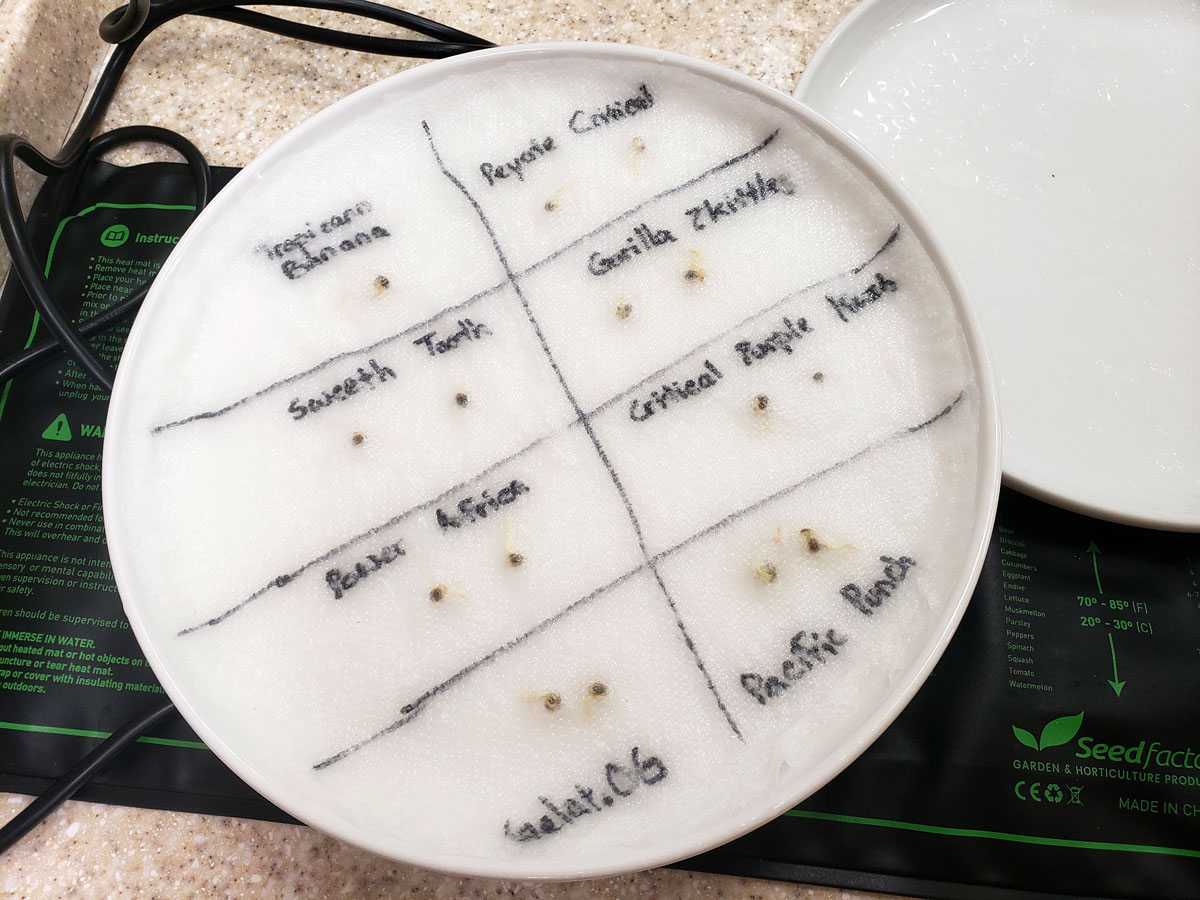
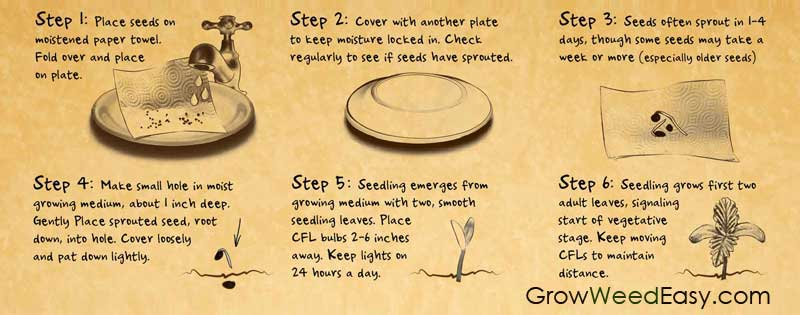
The image above is useful, but swap the plates for a jiffy bag/ re-sealable sandwich bag.
Let’s proceed to a step-by-step guide. You’ll go from preparing seeds and materials all the way to monitoring and transplanting.
Moistening the Paper Towel
With your seeds prepared, the next step involves readying the paper towel. Properly dampening the paper towel is critical for optimal seed germination, as it provides the necessary moisture for seeds without oversaturation. You can lightly dampen the paper towel, ensuring it is moist throughout without accumulating excess water.
Avoid soaking the paper towel, as overly wet conditions can lead to seed rot and hamper germination. Only use distilled, spring, rain or filtered water! Town/ Tap water can kill seeds.
Placing Seeds and Folding
Next, we’ll discuss how to properly place your seeds when starting seeds. Here are the steps to follow:
- Place the seeds on the top half of a damp paper towel.
- Leave about an inch of space between each seed to allow room for growth.
- After placing the seeds, fold the paper towel.
The folded paper towel with seeds should then be placed inside a Ziploc bag to maintain essential moisture for germination, simulating a mini greenhouse effect.
Finding the Ideal Location
But where should you place the bag? For optimal germination conditions, bags with paper towels and seeds should be placed in warm household areas, with good heat and humidity levels, like a south-facing window, bathroom, or laundry room. A Ziploc bag with a moist paper towel can create a mini greenhouse effect, which is crucial for maintaining the necessary moisture for seed growth.
Using a seedling heat mat under the seeds ensures a consistently warm germination environment, leading to a faster sprouting process. Some people put them on top of the fridge.
Monitoring and Transplanting
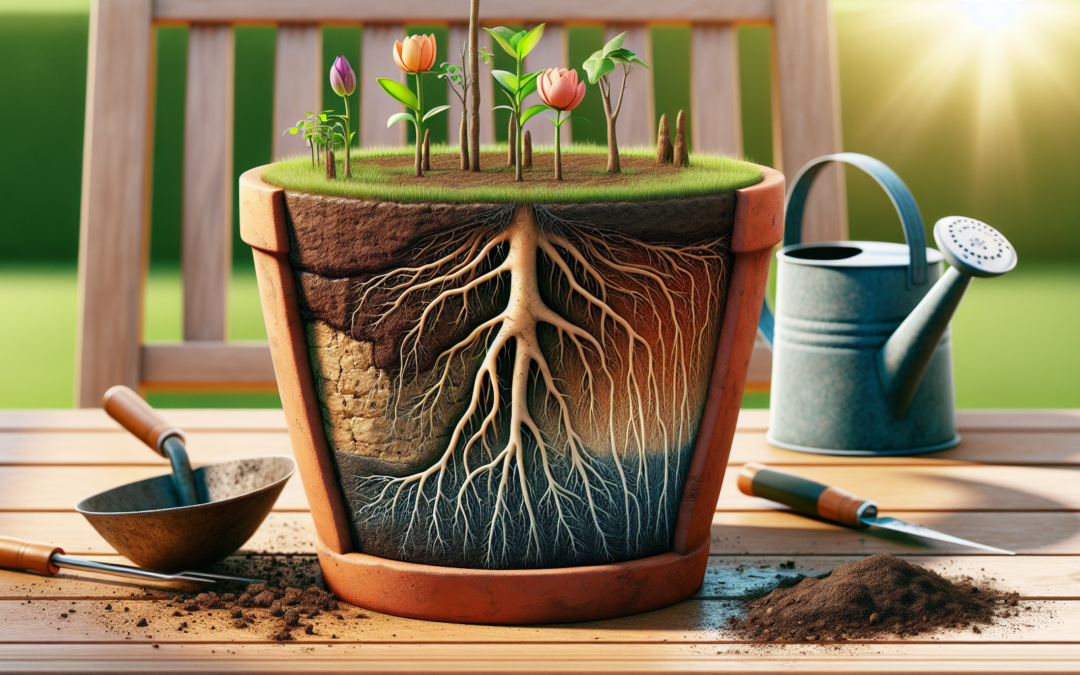
Monitoring and transplanting constitute the final step in the process. Daily monitoring of the seeds is required to check for emergence of a small white root and to ensure that the paper towel remains moist.
Once the radicle, which is the embryonic root, reaches an cm or two in length, it is the ideal time to transplant the germinated seed to soil. Handle the delicate seedling by the seed coat with tweezers or a gentle grip to avoid damage during transplantation.
Just to state the obvious: THE ROOT/ RADICLE GOES DOWN into the soil.
Pro tip!
If you are germinating several different varieties or strains, you can split the paper towel into sections using a pen, and clearly label each section.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite its apparent simplicity, the paper towel method can occasionally pose a few challenges. Let’s troubleshoot some common issues that may arise when you’re germinating seeds using this method.
Non-Germinating Seeds
Regardless of your best efforts, some seeds may fail to germinate. This can be due to several factors such as:
- The paper towel being either too wet, which can lead to rot
- The paper towel being too dry, failing to provide consistent moisture necessary for germination
- A lack of oxygen when seeds are sealed in a bag for several days using the paper towel method, which can inhibit germination.
- Toxic water (town water contains chlorine, fluoride and other chemicals).
Older seeds may also fail to germinate effectively due to decreased viability over time, particularly after the first couple of years and even within a few weeks of being germinated. This is why it’s important to consider other seeds as alternatives when planting, ensuring that seeds germinate successfully.
Root Growth in Paper Towels
Roots embedding into the paper towel is another frequent issue. To avoid this, it’s recommended to transfer the germinated seed to soil or another growing medium before the roots grow too long. Coffee filters are also recommended for the paper towel method to keep roots from growing into the fibers.
And if roots do become enmeshed in the paper, don’t panic. To transplant the cutting, simply trim around the base and place it in a pot along with the paper. This method allows for easy transfer and ensures successful growth.
🪖Helmet Head – Seedling Shell Stuck
Finally, you may observe a seedling shell adhering to the newly sprouted seedling, a condition commonly known as ‘helmet head’.
The seed coat will naturally detach when the first leaves, or cotyledons, emerge, so premature removal is not advised.
If it’s been a while and the shell is still stuck, you can gently soak just the seed coat in warm water to facilitate its removal without damaging the seedling.
Summary
In summary, the paper towel method for germinating cannabis seeds offers a host of benefits, from improved germination rates to easy monitoring and space efficiency.
It works well with various seeds, particularly those with longer germination times. By following the step-by-step guide and noting the troubleshooting tips, you can master this method and kickstart your gardening journey with ease and confidence.
Here is the technique again:
Step 1. Place the seeds in a cup of water to soak and leave them in a dark place for 6-12 hours. Ensure water temperature is between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius.
Step 2. Remove the seeds and place them on a hard plate 2cm apart from each other between two paper towels lightly dampened with water. Place another hard plate over the top to create a dome. Place in a warm dark place and ensure that the paper towels remain lightly moist.
Step 3. Seeds usually will germinate after 2-3 days, but can take up to a week so be patient. When the tap root emerges, it is time to plant the seed in a suitable growing medium.
Step 4. Be careful when transferring your seed as we recommend using tweezers. If using soil, place your seed gently into a 0.5 to 1 cm hole in the center of your growing medium. You will want the taproot facing down. Ensure your growing medium is kept wet and you should see a seedling within 2-5 days.
Important: Do not plant seeds directly in the ground or soil. In order to properly germinate, the plants need oxygen. Planting directly in the ground or soil may cause the seeds to rot before germination.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I plant seeds directly in the soil?
No, Planting directly in the ground or soil may cause the seeds to rot before germination.
Can I use the paper towel method for any kind of seeds?
Yes, you can use the paper towel method for various seeds, including vegetables, fruits, herbs, and flowers, especially those with longer germination times. Try it out with different seeds and see how it works for you!
What’s the ideal location for germinating seeds using the paper towel method?
The ideal location for germinating seeds using paper towels is a warm area with good heat and humidity levels, such as a south-facing window, bathroom, or laundry room. This environment will promote successful germination. You want a nice warm spot, but not too much direct sun.
My seeds are not germinating. What could be the problem?
Your seeds may not be germinating due to factors such as excessive moisture, inadequate oxygen, or their age.
The roots are growing into the paper towel. What should I do?
It’s best to carefully cut around the roots and plant the whole thing in a pot, including the paper. In the future, consider using a coffee filter to prevent this from happening.
The seedling shell is stuck on the newly emerged seedling. How can I remove it?
You can soak the seed coat in warm water to help remove it without harming the seedling. Be gentle!